Roman shipwrecks among latest seafloor discoveries near Alexandria
Nevine El-Aref
Three Roman shipwrecks and an ancient Egyptian votive bark to the god Osiris were discovered earlier this week on the Mediterranean seabed near the Egyptian city of Alexandria, along with a collection of smaller artefacts.
The finds were discovered during underwater excavations carried out by a joint mission from the Ministry of Antiqiuties' Underwater Archaeology Department and the European Institute of Underwater Archaeology in Abu Qir Bay and Alexandria's eastern harbour.
Three Roman shipwrecks and an ancient Egyptian votive bark to the god Osiris were discovered earlier this week on the Mediterranean seabed near the Egyptian city of Alexandria, along with a collection of smaller artefacts.
The finds were discovered during underwater excavations carried out by a joint mission from the Ministry of Antiqiuties' Underwater Archaeology Department and the European Institute of Underwater Archaeology in Abu Qir Bay and Alexandria's eastern harbour.
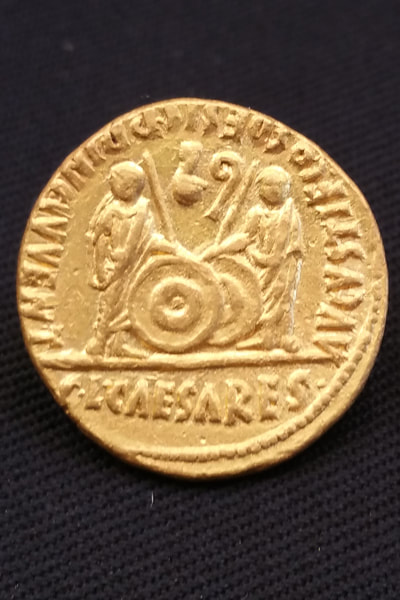
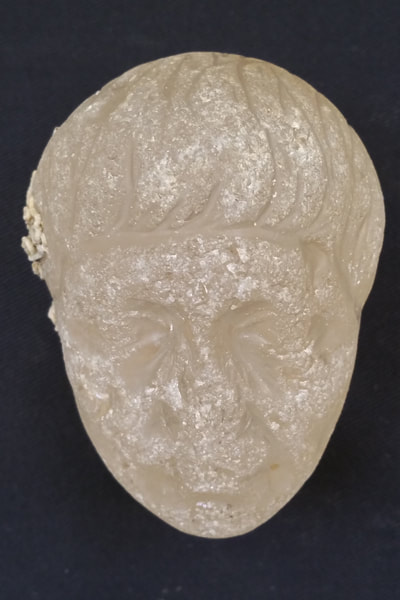
Mostafa Waziri, Secretary-General of the Supreme Council of Antiquities, told Ahram Online that the mission also uncovered a crystal Roman head probably depicting the Roman army commander Marc Antony and gold coins from the reign of Emperor Augustus.
Osama Al-Nahas, head of the Underwater Archeology Department at the ministry, explained that the eastern harbour still hides many treasures, and that evidence suggests a fourth shipwreck could yet be identified during the mission's next archaeological season in 2018.
The evidence, he told the Ahram Online, consists of large wooden beams and remains of pottery vessels, which may have been the cargo of a fourth ship.
Read More: english.ahram.org.eg/NewsContent/9/40/281925/Heritage/Ancient-Egypt/Roman-shipwrecks-among-latest-seafloor-discoveries.aspx
Osama Al-Nahas, head of the Underwater Archeology Department at the ministry, explained that the eastern harbour still hides many treasures, and that evidence suggests a fourth shipwreck could yet be identified during the mission's next archaeological season in 2018.
The evidence, he told the Ahram Online, consists of large wooden beams and remains of pottery vessels, which may have been the cargo of a fourth ship.
Read More: english.ahram.org.eg/NewsContent/9/40/281925/Heritage/Ancient-Egypt/Roman-shipwrecks-among-latest-seafloor-discoveries.aspx
Comment Form is loading comments...